Vegetable Cultivation Process According to VietGAP Standards (TCVN 11892)
VietGAP (Vietnamese Good Agricultural Practices) is the most widely encouraged and applied standard in current agricultural and aquacultural practices.
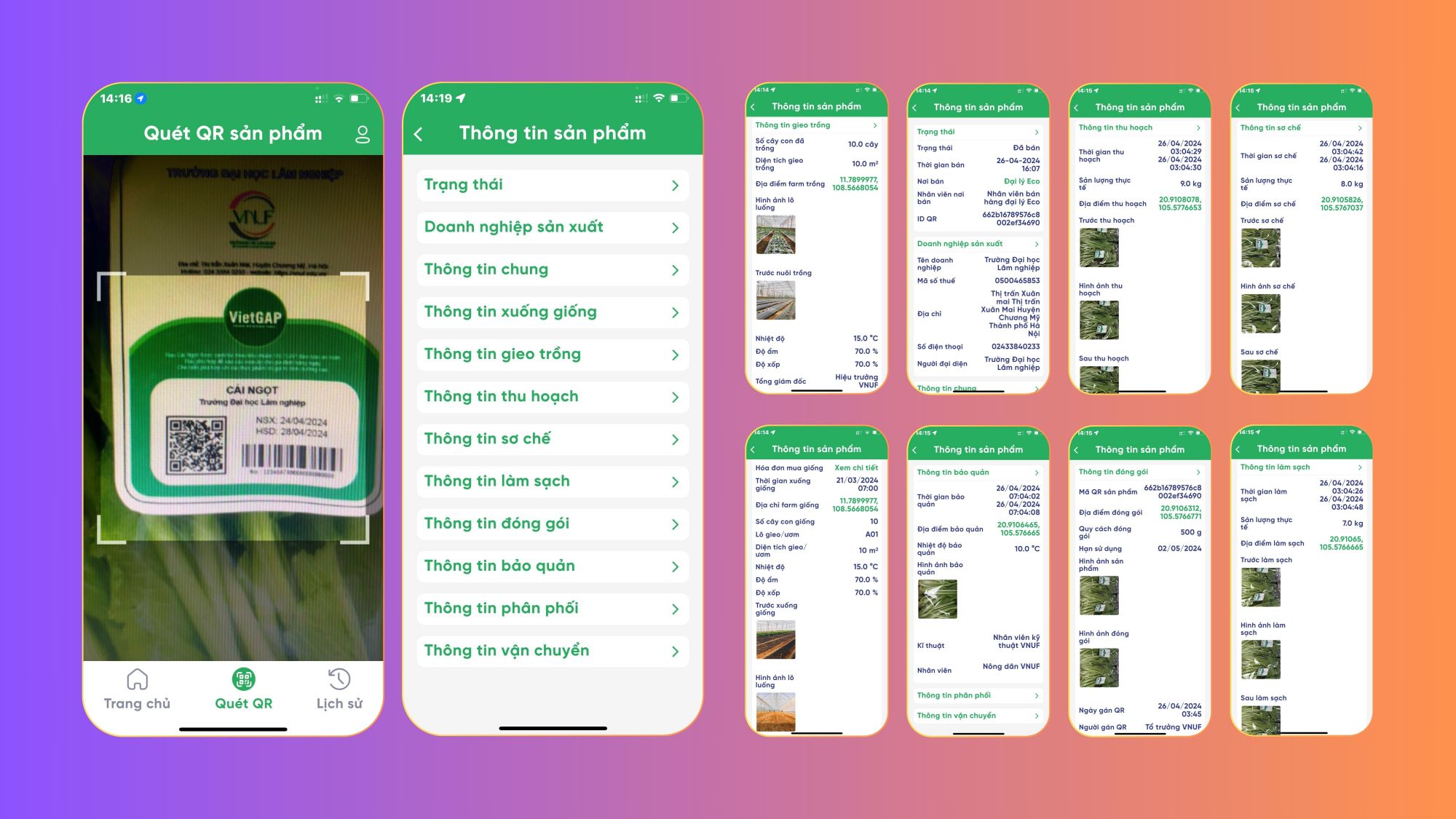
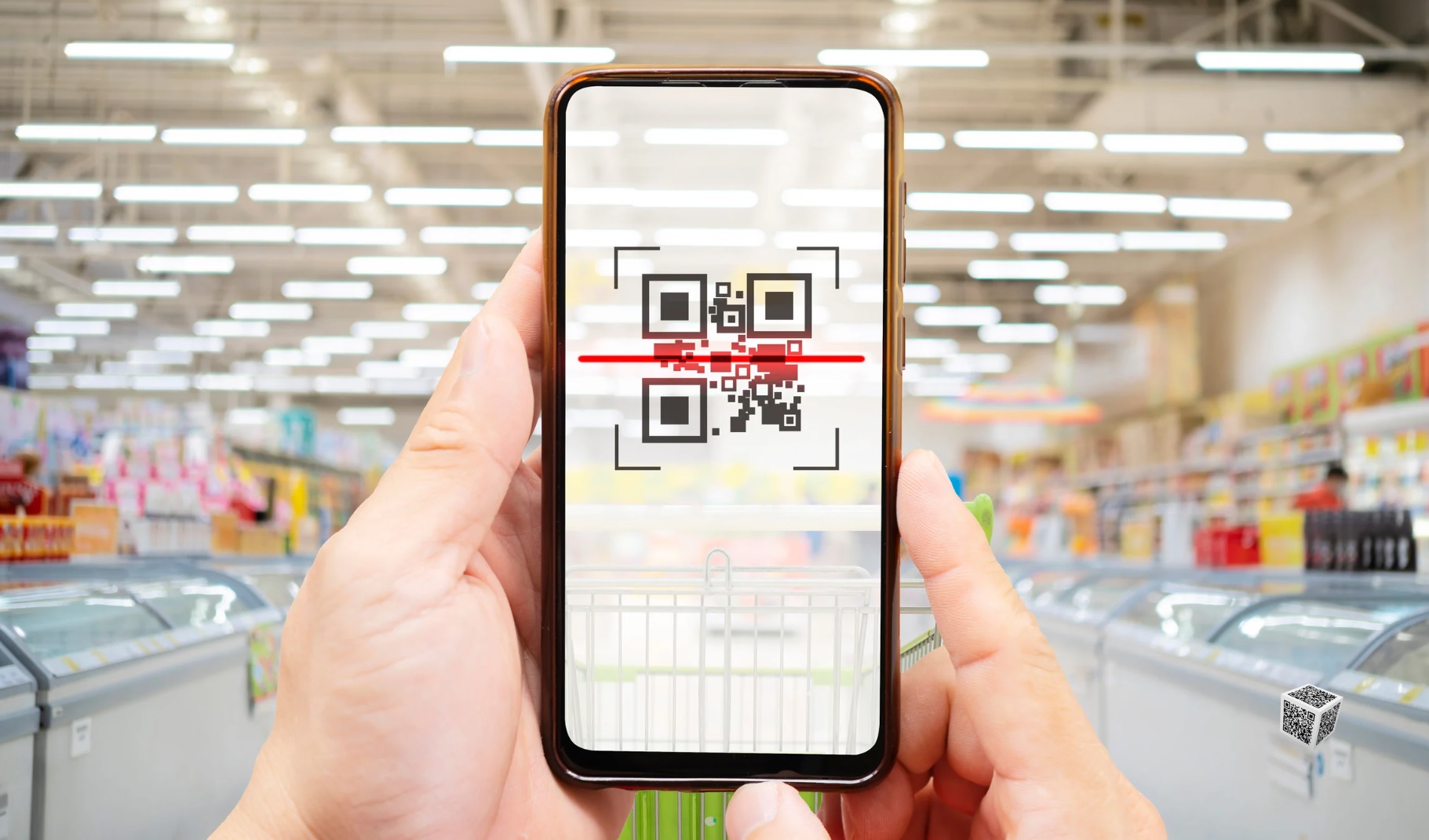
Image: Screenshot of the VN Check application tracing the origin of vegetables according to VietGAP standards
This article will guide you through 10 basic steps to practice cultivation according to VietGAP standards. Farms should pay attention and try to follow these steps:
1 - Select the Planting Soil
- Soil requirements: High land with good drainage, suitable for vegetable growth.
- Safe distance: At least 2 km away from areas with industrial waste and hospitals, and at least 200 m away from city household waste.
- Ensure there are no harmful chemical residues in the soil
2 - Irrigation Water Source
- Use water from unpolluted rivers or treated water.
- For lettuce and herb vegetables, use well water.
- Use clean water for mixing foliar fertilizers and pesticides
3 - Seed Selection
- Seed origin: Know the production history of the seeds. Imported seeds must pass quarantine inspection.
- Seed quality: Choose good seeds and healthy seedlings free from pests and diseases.
- Pre-sowing treatment: Seeds must be treated with chemicals or heat to eliminate pests and diseases.
4 - Fertilization
- Prioritize the use of composted organic fertilizers.
- Avoid using uncomposted manure or diluted fresh manure.
- Chemical fertilizers: Apply the right amount according to the requirements of each type of vegetable, ending application at least 15 days before harvest.
5 - Pest and Disease Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM):
- Rotate crops appropriately.
- Choose resistant varieties.
- Maintain healthy plants and field hygiene.
- Use manual labor for pest control and biological agents
Plant Protection Products (PPP):
- Use only when necessary and choose less toxic chemicals.
- Prioritize biological pesticides.
- Follow guidelines on usage and harvest intervals.
6 - Use of Other Measures
- Net houses, greenhouses: Provide protection against pests, weeds, frost, drought, and shorten growth periods.
- Nylon sheets: Cover the soil to control pests, weeds, and save irrigation water.
7 - Harvesting
- Harvest at the right ripeness and according to the requirements of each type of vegetable.
- Remove old, withered leaves and diseased or deformed fruits.
- Thoroughly wash vegetables with clean water and store in clean bags.
8 - Processing and Inspection
- After harvesting, vegetables are sorted and cleaned in a processing room.
- Wash thoroughly with clean water and use clean bags for storage.
9 - Transportation
- Vegetables are sealed and transported to stores or consumers within 2 hours to ensure hygiene and safety.
10 - Preservation and Use
- Store vegetables at 20°C in the store; storage time should not exceed 2 days.
- Safe vegetables can be used immediately without soaking in saltwater or other cleaning agents.
These are the 10 steps for practicing Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) with various vegetables and fruits according to VietGAP standards. During implementation, farms should focus on correct techniques, ensure a safe working environment, and prioritize food safety by avoiding chemicals, bacteria, or physical contaminants to ensure traceability from production to consumer. Consumers can scan the QR code on the VN Check app to view the entire process of cultivation, harvesting, packaging, and distribution of the product.
CALL 024 6258 6258 NOW FOR GUIDANCE.










.jpg)
