Why QR Codes Instead of Other Data-Carrying Materials?
In a previous article, we clarified how QR codes work. The undeniable advantages of QR codes include: low cost, ease of application on various materials, robust encryption that is hard to hack, and the ability to be used both online and offline.
According to Article 5 of Circular 02/2024/TT-BKHCN issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology on March 28, 2024, effective from June 1, 2024, it is stipulated:
- Organizations and individuals implementing product traceability must use product traceability codes and location traceability codes that comply with the National Standard TCVN 13274:2020 Traceability - Guidelines for Code Formats used in Traceability, as published by the Ministry of Science and Technology before use.
- Organizations and individuals implementing product traceability must use data-carrying materials that comply with the National Standard TCVN 13275:2020 Traceability - Data Carrier Formats, as published by the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Data carriers must be affixed, printed, attached, embossed, engraved directly on the product, goods, or product packaging, or on other materials attached to the product or packaging, ensuring that the data can be read by devices.

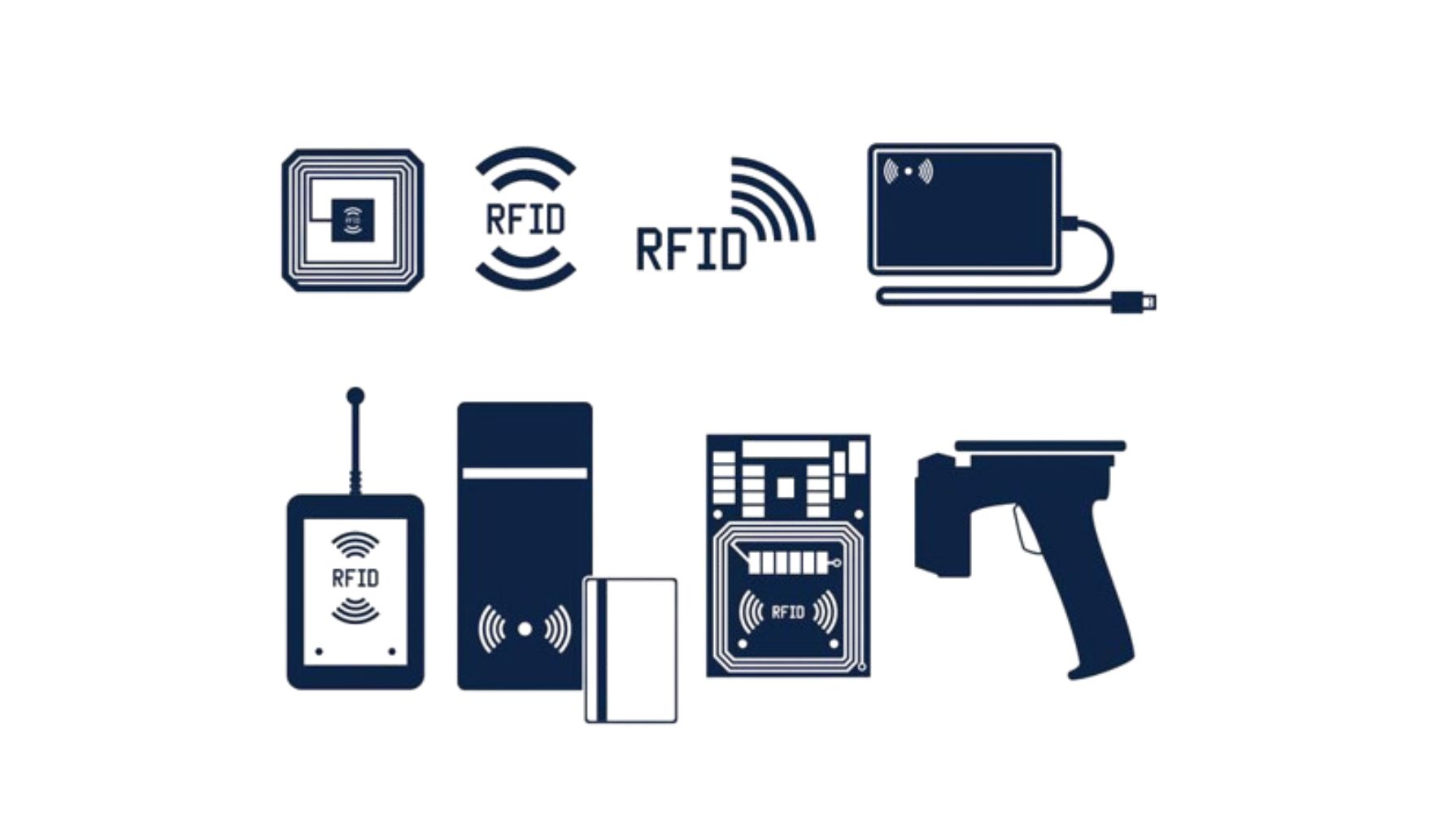
According to TCVN 13275:2020 - Section 3 - Point 3.2, barcodes, RFID tags, and OCR character strings are permitted for use in traceability. As detailed in our previous article on RFID technology, we discussed its shortcomings and potential applications. While RFID technology holds significant value, we must also consider its economic efficiency, especially in agriculture and food sectors. In the future, RFID may be used for product and goods data tagging, but it is unlikely to be our top priority due to its inherent drawbacks.
Here’s what we can achieve with QR codes:
1 - Widespread Usage: QR codes are quite popular and are integrated into almost all mobile devices. There’s no reason not to leverage the customer base of over 4 billion users. According to the 2023 Mobile Internet Connectivity Report by GSMA, 55% of the global population (around 4.3 billion people) currently uses smartphones.
2 - Ease of Implementation: QR code application is straightforward and suitable for all materials and environments. QR codes can be applied across various business sectors including marketing, industry, postal services, education, and with VN Check, agriculture and traditional medicine.
3 - Cost-Effectiveness: Creating a QR code is free or very inexpensive. With VN Check, we can provide QR code files in two formats (PDF and XLS) to clients, allowing customization for anti-counterfeiting measures using artificial intelligence and product traceability.
In addition to these three reasons, there’s another reason we are focusing on QR codes: their multidimensional barcode application in the sustainable virtual environment - Metaverse. You may be curious about the concept of multidimensional QR codes that we plan to introduce. This is currently under research and development. We will present the multidimensional QR code once we have fully explored the capabilities of the traditional two-dimensional QR code.









.jpg)

